Getting started using the API
The following text describes the use of the HTTP API. Using the .NET API will follow the same logic.
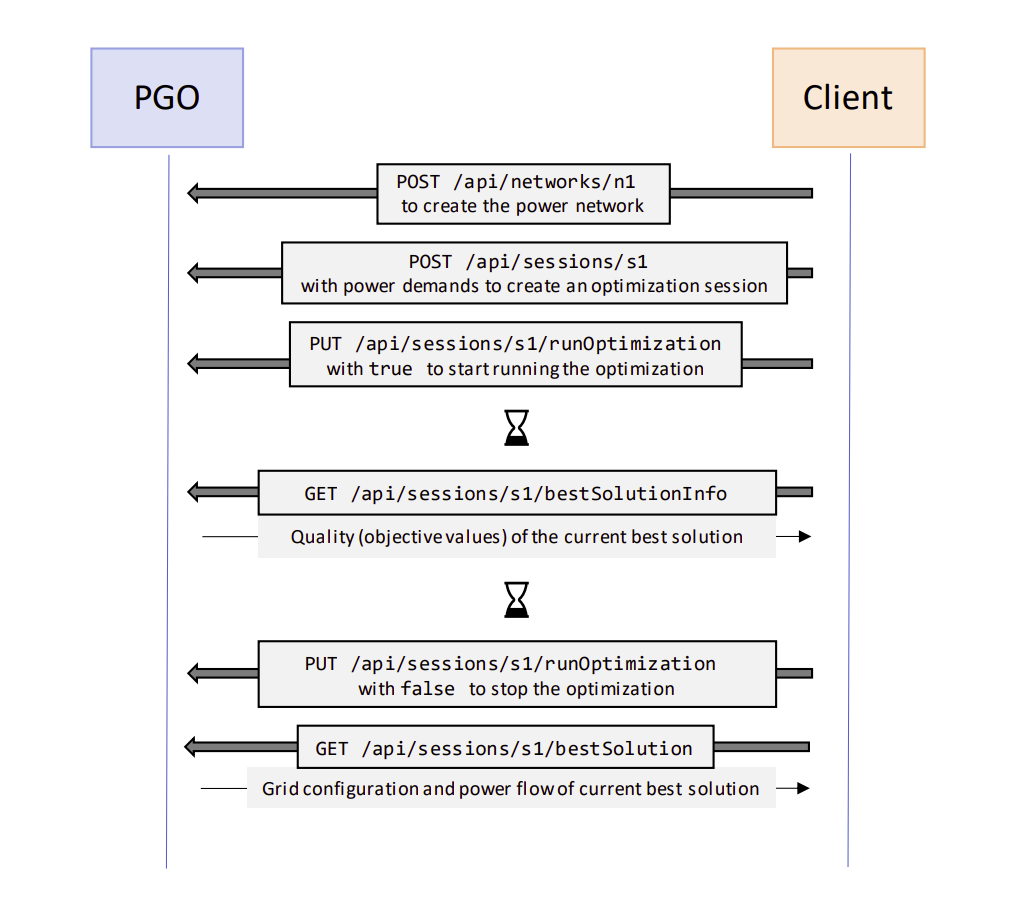
In an actual deployment, the proper endpoints should be used, but it is also possible to test through Swagger. Here we illustrate the intended flow of the service.
POST /api/networks/n1with a network JSON file in the request body to load a power network and name itn1.GET /api/networks/n1/analysiscan optionally be called to analyse the loaded network and flag any issues with the network structure that might cause problems for the optimization.POST /api/sessions/s1to create a session with ids1and give a forecast JSON file in the request body. Here, a start configuration JSON file may also be given.PUT /api/sessions/s1/runOptimizationwithtruein the request body to start the optimization.- Wait a minute or so. The optimizer works iteratively, and the current state can be polled with
GET /api/sessions/s1or (for more details)GET /api/sessions/s1/bestSolutionInfo. - When a solution is desired, it can be retrieved with
GET /api/sessions/s1/bestSolution. - To halt the solver work,
PUT /api/sessions/s1/runOptimizationwith false in the request body.
See also the full API reference.
